Bile imbalance liver cancer has emerged as a significant concern in liver cancer research, linking the metabolic processes of bile acids to their role in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), the most prevalent form of liver cancer. Recent studies have highlighted how disruptions in bile acid homeostasis can lead to liver diseases, triggering inflammation and fostering an environment conducive to cancer development. Researchers have pinpointed a critical molecular switch in bile acid metabolism that sheds new light on potential treatment interventions, enhancing our understanding of the YAP FXR relationship in liver pathology. Understanding the connection between bile acids and cancer not only opens doors for innovative liver disease treatments but also emphasizes the need for continued exploration in this vital area of study. As we delve deeper into the regulatory mechanisms of bile acids, the hope is to mitigate the devastating impacts of liver cancer.
Liver dysfunction can be intricately connected to an imbalance in bile acids, leading to dire consequences such as hepatocellular carcinoma. This form of liver cancer has garnered attention due to its rising prevalence and the critical role bile plays in nutrient digestion and metabolic regulation. Investigating the relationship between bile acids and cancerous growths is crucial, particularly understanding how the Hippo/YAP signaling pathway influences bile acid metabolism. By exploring therapeutic avenues that target this pathway, researchers aspire to enhance liver health and provide effective strategies for liver disease treatment. As our knowledge expands, the promise of developing successful interventions becomes increasingly tangible.
Understanding Bile Imbalance and Liver Cancer
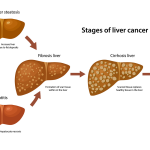
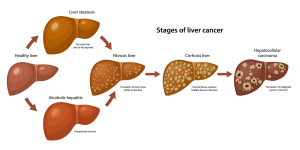
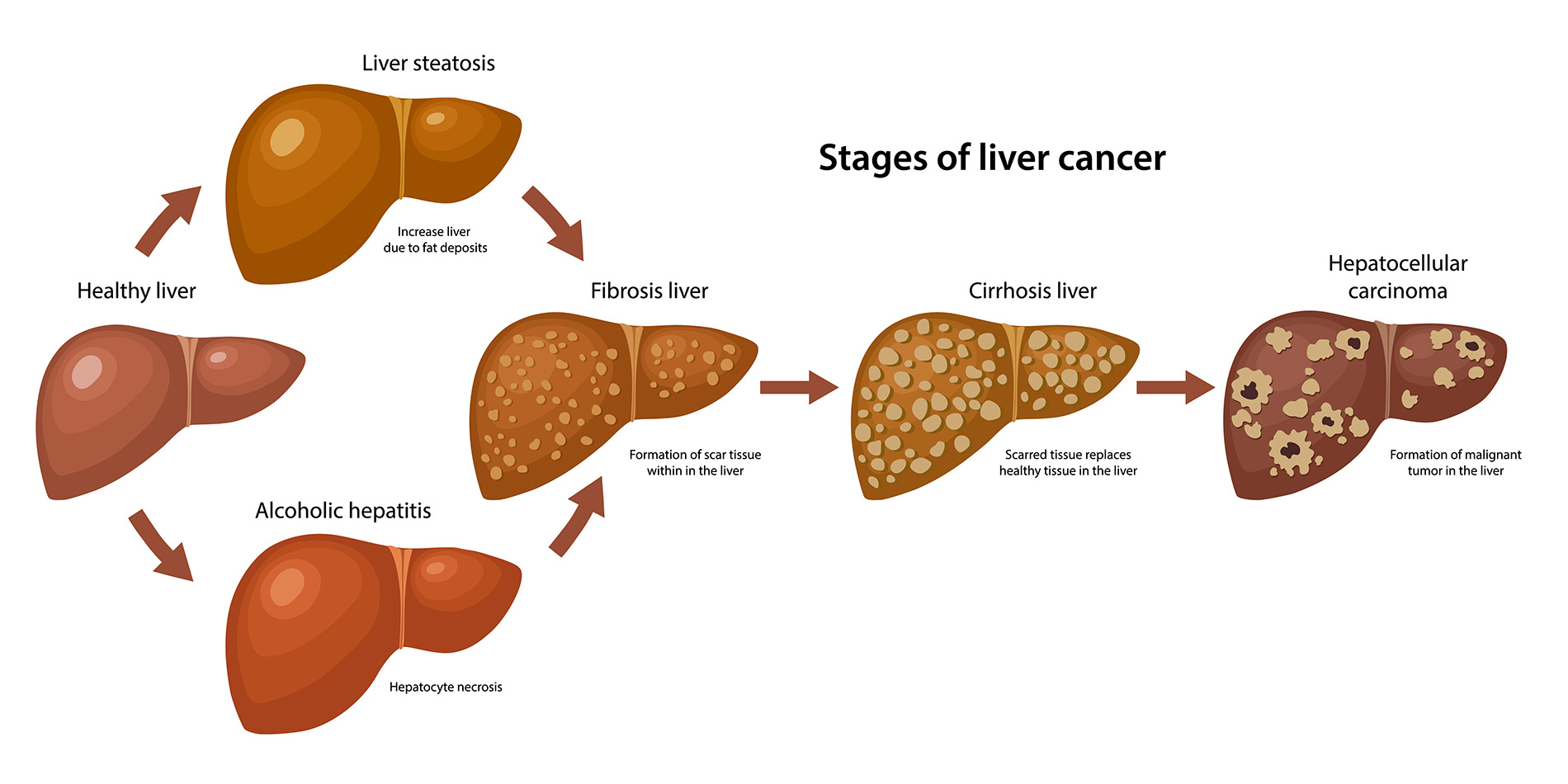
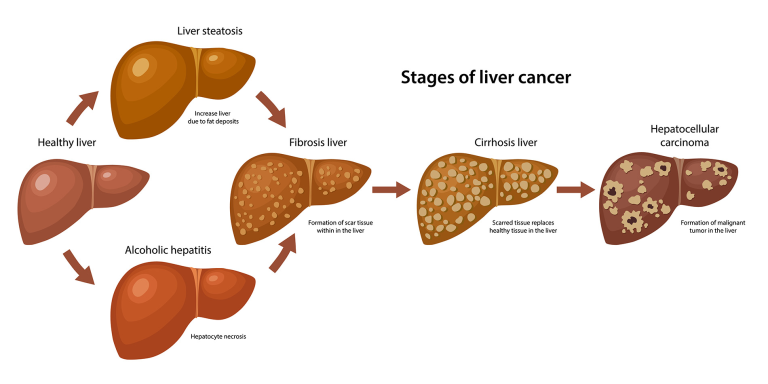
Recent research has illuminated a critical link between bile imbalance and liver cancer, particularly hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), which is the most prevalent type of liver cancer. Bile, produced by the liver, plays an essential role not only in fat digestion but also in regulating several metabolic processes. Imbalances in bile acids can lead to significant liver injury, inflammation, and, ultimately, the development of HCC. Studies suggest that the disruption in normal bile acid levels may act as a precursor to various liver diseases, highlighting the need for further investigation into bile acid metabolism and its implications for liver cancer research.
To better understand the mechanisms behind this link, researchers are focusing on key molecular pathways involved in bile acid regulation. A fundamental aspect of this research involves the Hippo/YAP signaling pathway, which plays a critical role in cell growth and metabolism. The discovery that YAP functions as a repressor of the FXR (Farnesoid X receptor), a vital component for maintaining bile acid homeostasis, sheds light on how overproduction of bile acids occurs. This overproduction could lead to conditions favorable for the development of liver cancer, thereby emphasizing the importance of maintaining optimal bile balance for liver health.
The Role of the YAP-FXR Relationship in Liver Disease Treatment
One of the most promising areas of liver disease treatment lies in understanding the complex interaction between YAP and FXR. Recent studies have shown that YAP can inhibit the function of FXR, leading to the dysregulation of bile acid metabolism. This inhibition results in elevated bile acid levels, which can cause liver fibrosis and potentially trigger hepatocellular carcinoma. By exploring this critical relationship, researchers may identify new therapeutic strategies aimed at enhancing FXR function, thus mitigating the damaging effects of bile acid accumulation in the liver.
Targeting the YAP-FXR relationship opens up innovative avenues in liver cancer treatment. Interventions that can either inhibit YAP’s repressor activity or promote FXR function could lead to improved bile acid regulation. For instance, activating FXR, inhibiting HDAC1 involved in YAP’s repression, or increasing the activity of bile acid export proteins like BSEP have shown promise in reducing liver damage and halting cancer progression in experimental models. As our understanding deepens, pharmacological interventions aimed at correcting bile imbalance could play a pivotal role in the future of liver disease treatment.
Exploring Bile Acids and Cancer: Implications for Research
The connection between bile acids and cancer is a burgeoning field of research, particularly in relation to liver cancer. As bile acids are not only crucial for digestion but also act as signaling molecules that influence various metabolic pathways, researchers are beginning to unravel how imbalances can contribute to oncogenesis. Recent studies have suggested that alterations in bile acid profiles may serve as biomarkers for liver disease progression, highlighting their potential diagnostic role in hepatocellular carcinoma. This opens up exciting new opportunities for early detection and personalized medicine approaches in liver cancer treatment.
Additionally, understanding the biochemical pathways through which bile acids operate provides insight into potential therapeutic targets. The relationship between bile acids and tumorigenesis indicates that by modulating bile metabolism, it may be possible to develop strategies that prevent or slow down the advancement of liver cancers. Ongoing liver cancer research continues to investigate how these pathways can be manipulated to provide clinical benefits, aiming to establish new, effective liver disease treatment options.
Molecular Mechanisms in Liver Cancer Development
The intricate molecular mechanisms contributing to liver cancer development, particularly in cases of bile imbalance, deserve close scrutiny. Research has revealed that the Hippo/YAP pathway is critically involved in regulating liver cell growth and, when dysfunctional, can lead to liver tumors including hepatocellular carcinoma. By understanding how YAP promotes tumor formation through its repressive interactions with FXR, scientists are illuminating new paths for potential therapeutic approaches. This molecular understanding is paramount as it aligns with the aim of developing targeted therapies that can counteract the dysregulation often seen in liver diseases.
Furthermore, comprehensive studies exploring the relationship between bile acids, liver inflammation, and tumorigenesis are vital. Disturbances in bile acid homeostasis have been linked to various liver diseases, resulting in chronic inflammation and subsequent tumor development. These findings underscore the critical need for innovative research aimed at clarifying the role of bile acids and their molecular interactions in liver cancer progression, which could pave the way for novel treatments aimed at ameliorating liver diseases.
Importance of Bile Acid Homeostasis in Liver Health
Maintaining bile acid homeostasis is essential for overall liver health, as well as for preventing liver diseases such as hepatocellular carcinoma. The liver’s ability to produce and regulate bile acids is crucial for effective digestion and metabolic function. Disruptions in bile acid levels can lead to a cascade of events resulting in liver damage, fibrosis, and the potential onset of cancer. Understanding the mechanisms that regulate bile acids is therefore vital for developing strategies aimed at preserving liver function and preventing liver-related diseases.
Efforts to enhance bile acid regulation through nutritional and pharmacological interventions may provide new approaches to liver disease treatment. By focusing on the pathways involving FXR and YAP, and exploring how lifestyle changes can impact bile acid metabolism, patients may have access to novel therapies that could prevent liver disease and ensure better health outcomes. This holistic approach to managing bile acid levels can significantly contribute to the prevention of liver cancer and the promotion of liver health.
Potential Pharmacological Interventions for Liver Damage
The findings surrounding bile imbalance and liver cancer have opened the door to exploring pharmacological interventions that target key molecular pathways to prevent liver damage. Potential treatments may focus on enhancing FXR signaling, which is vital for maintaining bile acid homeostasis. If future research confirms that stimulating FXR can reduce bile acid accumulation and its associated adverse effects, medications designed to enhance FXR function could emerge as a frontline defensive strategy against liver diseases, including hepatocellular carcinoma.
Moreover, additional therapeutic strategies might involve agents that inhibit YAP activity, thus restoring the natural balance of bile acids in the liver. Treatments that boost bile acid export mechanisms or enhance the metabolism of bile acids may also offer protective benefits. As research continues to unveil the intricate relationships between liver enzymes, bile acids, and cancer pathways, the development of targeted pharmacological treatments will likely play a significant role in the fight against liver cancer.
Future Directions in Liver Cancer Research
Liver cancer research is at a pivotal point in exploring the various molecular mechanisms related to bile imbalance and disease progression. As scientists uncover the complexities of the Hippo/YAP signaling pathway and its role in bile acid regulation, future studies will likely delve deeper into how these insights can be translated into effective clinical applications. Investigating the dynamic interactions among bile acids, liver inflammation, and tumor growth not only enhances our understanding of liver disease but also sets the stage for innovative therapeutic strategies.
Additionally, interdisciplinary collaborations between molecular biologists, clinicians, and pharmacologists will be essential for translating these findings into real-world applications. Developing targeted therapies that specifically address the molecular imbalances observed in liver cancer will be a primary focus moving forward. As research in liver cancer continues to evolve, the integration of personalized medicine and a deeper understanding of bile metabolism will play crucial roles in advancing liver disease treatment options.
The Implications of Research on Bile Acids in Clinical Practice
The clinical implications of ongoing research into bile acids and their link to liver diseases are profound. Understanding the role of bile acid metabolism in the context of liver health can lead to the development of diagnostic tools that allow for early detection of liver dysfunction and cancer. As studies highlight the association between bile imbalance and the progression of hepatocellular carcinoma, healthcare providers may be better equipped to screen high-risk individuals proactively, ensuring timely interventions.
Furthermore, integrating bile acid profiling into clinical practice can facilitate personalized treatment options tailored to individual metabolisms. This approach may enhance the effectiveness of existing liver disease treatments and guide the exploration of new pharmacological therapies targeting the metabolic pathways related to bile acid regulation. The translation of research findings into clinical practice holds significant promise for improving patient outcomes in liver cancer and other liver-related conditions.
Conclusions: The Path Forward in Liver Health
In conclusion, the relationship between bile imbalance and liver cancer presents a promising area of inquiry with the potential to revolutionize liver health management. Continued research aimed at understanding the molecular intricacies of bile acid regulation and its implications for disease progression is essential. Unlocking the secrets of the Hippo/YAP pathway and its impact on bile acid homeostasis could pave the way for novel therapeutic approaches that address the root causes of liver diseases.
Ultimately, prioritizing liver health through a comprehensive understanding of bile metabolism is vital for preventing liver cancers such as hepatocellular carcinoma. By fostering interdisciplinary collaboration in research and clinical settings, we can develop innovative strategies to combat liver disease and enhance the quality of care for individuals affected by liver conditions. The future of liver cancer research and treatment is bright, anchored in the insights gained from understanding bile acids and their pivotal roles.
Frequently Asked Questions
How is bile imbalance related to liver cancer?
Bile imbalance plays a crucial role in the development of liver cancer, particularly hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Disruptions in bile acid production can lead to liver injury and inflammation, which are precursors to cancer. Studies indicate that imbalances in bile acids stimulate cell signaling pathways linked to tumor development.
What are the implications of liver cancer research on bile acids?
Liver cancer research highlights the importance of bile acids in maintaining liver health. An imbalance can cause metabolic disruptions, leading to hepatocellular carcinoma. Ongoing studies are revealing potential treatments focused on regulating these bile acids and enhancing liver function.
What is the YAP-FXR relationship in liver cancer?
The YAP-FXR relationship is significant in understanding bile imbalance and liver cancer. YAP, a signaling molecule, represses FXR, which is crucial for bile acid metabolism. This repression leads to bile acid overproduction, contributing to liver damage and HCC. Targeting this interaction offers potential therapeutic avenues.
How can bile acids impact liver disease treatment?
Bile acids can significantly impact liver disease treatment. Research shows that restoring bile acid homeostasis might be a key strategy for treating liver conditions, including hepatocellular carcinoma. Therapeutics that enhance FXR function or promote bile acid excretion are being explored to combat liver damage and malignancies.
What role does bile play in liver health and cancer?
Bile serves as a detergent for fat digestion and has hormone-like functions that regulate metabolic processes. An imbalance in bile acids can lead to liver inflammation and disease, thereby increasing the risk of hepatocellular carcinoma. Understanding bile’s role can inform new treatment strategies.
How does dysregulation of bile acids lead to liver injury?
Dysregulation of bile acids leads to liver injury by causing an accumulation of toxic bile acids. This buildup can trigger inflammation and fibrosis, which are critical steps in the progression to hepatocellular carcinoma. Hence, maintaining bile balance is essential for liver health.
What are potential pharmacological solutions in treating bile imbalance and liver cancer?
Potential pharmacological solutions for treating bile imbalance and liver cancer include drugs that stimulate FXR activity, enhance bile acid excretion, or inhibit specific pathways associated with YAP. These treatments aim to restore balance and prevent cancer progression.
What are the key findings of the study regarding bile acids and liver cancer?
Key findings from the study indicate that imbalances in bile acids lead to liver damage and promote the development of hepatocellular carcinoma. The study identified a molecular switch involving YAP and FXR critical for this process, paving the way for novel treatment strategies.
Can lifestyle changes impact bile imbalance and liver cancer risk?
Yes, lifestyle changes such as a healthy diet, regular exercise, and avoiding alcohol can positively influence bile balance and reduce the risk of liver cancers like hepatocellular carcinoma. Maintaining liver health through these modifications is crucial.
What is the significance of studying bile acids in liver disease?
Studying bile acids is significant in liver disease as they play a role in metabolic regulation and liver function. Understanding their impact on liver health can lead to innovative treatment strategies for various liver conditions, including liver cancer.
| Key Points |
|---|
| A new study links bile imbalance to liver cancer, specifically hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). |
| Bile acids are crucial for fat digestion and also play hormone-like roles in metabolism. |
| YAP, a signaling molecule, was found to repress FXR, a vital bile acid sensor. |
| This repression leads to bile acid overproduction, causing liver injury and inflammation. |
| Targeting the YAP-FXR pathway may present new treatment options for liver damage and cancer. |
| Yingzi Yang, the study’s lead, highlights the potential for pharmacological solutions to enhance FXR function. |
Summary
Bile imbalance liver cancer is a significant concern, as recent studies have illuminated the connection between disrupted bile acid regulation and the development of liver cancer, particularly hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Researchers have identified the role of the YAP signaling pathway in this process, highlighting its repressive effects on crucial bile acid sensors. The findings offer promising directions for potential treatments by aiming to correct this bile imbalance. As our understanding grows, addressing bile imbalance could become key in therapeutic strategies against liver cancer.