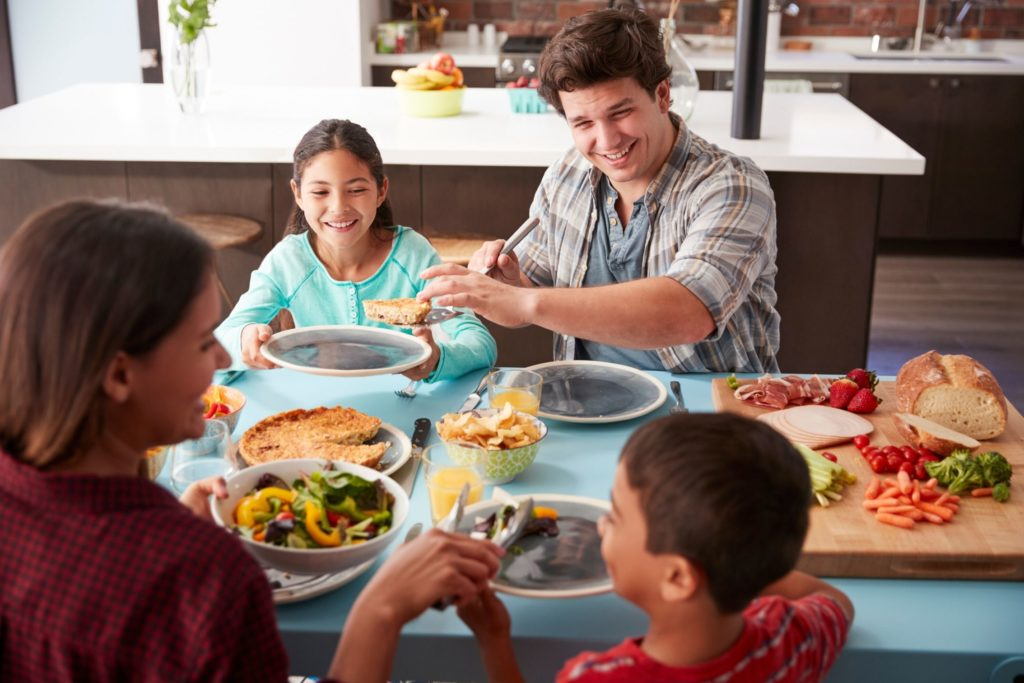
Shared meals and happiness have long been intertwined, illuminating how dining together fuels social connections and enhances overall well-being. Numerous happiness statistics reveal that individuals who regularly enjoy meals with others report greater satisfaction in both life and emotional expression. This phenomenon extends across diverse groups and cultures, suggesting that mealtime impact on well-being is universally significant. However, recent trends indicate a concerning shift in dining habits, with more Americans choosing to eat alone, impacting their mental health. Emphasizing the meal sharing benefits could pave the way for improved social bonds and a collective rise in happiness.
The joy of gathering around a table to share food transcends mere culinary enjoyment; it reflects deeper connections forged during dining experiences. Research shows that communal eating patterns can significantly influence mental wellness, contributing to enhanced joy and fulfillment. As individuals increasingly opt for solitary mealtimes, the importance of fostering group dining traditions gains prominence in discussions about community health. Observations about collective eating behaviors shed light on the necessity for social engagement in cultivating emotional happiness. Understanding these dynamics might encourage both individuals and societies to prioritize shared mealtimes as a pathway to improved mental health.
The Connection Between Shared Meals and Happiness
Dining with others has emerged as a significant contributor to overall happiness and life satisfaction. Recent research highlights that individuals who frequently share meals report higher levels of positive emotions compared to those who dine alone. This connection underscores the importance of social connections during mealtimes, as the simple act of sharing a meal can enhance feelings of community and belonging. By gathering around the table, people not only nourish their bodies but also strengthen bonds that contribute to well-being.
Moreover, the evidence suggests that shared dining experiences can influence mental health positively. Happiness statistics indicate that as we gather for meals, the interactions we have with family and friends can alleviate feelings of depression and anxiety. The act of sharing experiences during meals creates lasting memories and fosters a dynamic space for communication. In essence, shared meals become a tool for individuals to enhance their emotional health, making them a significant factor to consider in discussions about mental well-being.
Dining Habits and Their Impact on Mental Health
Our dining habits play a crucial role in shaping our mental health. A shift from communal eating towards solitary dining, particularly in the United States, has been associated with rising levels of social isolation and declining well-being. Research shows that as more individuals report eating alone, concerns on how this behavior impacts mental health grow. Experts argue that endorsing a culture of shared meals can combat loneliness and its negative effects, improving overall happiness and life satisfaction.
In understanding the dynamics of our dining habits, it becomes imperative to recognize mealtime as an opportunity for connection. Frequenting restaurants or hosting dinner parties not only fuels culinary enjoyment but also fosters social interactions that can enhance mental health. By carefully evaluating our arrangements around meals, we can integrate practices that prioritize shared experiences, ultimately shaping a more connected and happier society.
The Role of Mealtime in Strengthening Social Connections
Mealtimes serve as an essential backdrop for nurturing social connections among individuals. Whether it’s a family dinner, a lunch meeting with colleagues, or a potluck with friends, sharing a meal often leads to deeper conversations and shared experiences. This bond developed through meal sharing can significantly boost feelings of happiness and connection, which is vital for maintaining mental well-being. The more we come together, the stronger these relationships grow, acting as a natural antidote to feelings of isolation.
Research implies that those who engage in communal dining regularly are likely to strengthen their social networks. The benefits extend beyond mere satisfaction; they resonate into the emotional domain, promoting resilience against stress and anxiety. In revitalizing our dining habits to include more shared meals, we are not only feeding our bodies but also forging connections that contribute to a healthier mental state and increased longevity.
Mealtime Impact on Well-Being: A Study of Trends
Examining the mealtime impact on well-being reveals a troubling trend: more Americans are spending increasing amounts of time eating alone. A recent study points out that about 25% of Americans now report dining solo, an alarming increase that could have detrimental effects on mental health and happiness. This shift indicates that many people may be missing out on the enriching experience that comes from breaking bread together, which can serve as a critical catalyst for happiness.
Moreover, the implications of solitary dining extend beyond personal satisfaction. The increasing trend of eating alone could indicate broader societal changes, where the fabric of community life might be at risk of fraying. It underscores the urgent need for initiatives that promote communal dining experiences to counterbalance this trend. By encouraging shared meals, we may begin to reverse some of the negative effects on mental health associated with social isolation.
Exploring the Benefits of Meal Sharing
Meal sharing comes with a myriad of benefits, particularly in enhancing happiness and fostering strong social bonds. Engaging in shared meals can contribute positively to our emotional states by reducing stress levels and promoting a sense of belonging. The unique joy that comes from enjoying delicious food in the company of others nurtures friendships and strengthens family ties, establishing a supportive network that is essential for mental well-being.
Furthermore, studies highlight that meal sharing can also encourage healthier eating habits. When people dine together, there is often an increased awareness of nutrition and cooking practices, which can lead to better health outcomes. Thus, the benefits of meal sharing ripple outwards—from boosting happiness statistics to improving physical health—making it a vital aspect of both social interactions and public health.”}]},{
Policy Implications for Meal Sharing
As research continues to link meal sharing with higher levels of happiness, policymakers have begun to recognize the importance of promoting communal dining initiatives. Developing community programs that encourage shared meals—such as community dinners, cooking classes, and even public dining spaces—could play a crucial role in enhancing overall well-being. Such initiatives can help combat social isolation by providing platforms for personal interaction and connection.
The potential for policies focused on meal sharing to improve mental health demonstrates the broader implications of our dining habits. By investing in programs that encourage community engagement around food, governments can address issues of loneliness while simultaneously promoting healthy eating. Thus, facilitating more shared meals could mean investing in a happier, healthier population, emphasizing the importance of communal experiences in everyday life.
Shared Meals: A Window into Happiness Evaluation
Shared meals, as a tangible indicator, present researchers with a unique perspective on evaluating happiness. Traditional indicators such as income and employment status have long been utilized; however, the emerging evidence suggests that the quality of one’s social interactions—as seen in shared meals—is just as indicative, if not more so, of well-being. Researchers are now focusing on how these dining experiences contribute to happiness levels across diverse demographics.
Additionally, the challenge of measuring happiness can benefit from the clarity offered by meal sharing statistics. Unlike subjective happiness ratings, counting shared meals can provide straightforward data that reflects an individual’s social life. This simplification can prove invaluable for social scientists and public policy advisors aiming to craft interventions that foster communal bonds, preemptively enhancing the well-being of communities.
Cultural Contexts of Shared Meals and Well-Being
Exploring shared meals across various cultural contexts reveals diverse meanings and practices that contribute uniquely to happiness. In many cultures, communal dining is a deeply ingrained tradition, fostering connections that are pivotal for maintaining familial and social ties. The rituals and customs associated with sharing meals not only serve to sustain relationships but also to promote a sense of identity and belonging, which are crucial for mental well-being.
Moreover, understanding these cultural nuances allows for a more comprehensive examination of the benefits linked to shared dining experiences. By delving into diverse dining habits, researchers can highlight practices that nurture happiness across different populations, emphasizing the universal importance of coming together for meals. This cultural perspective enriches the dialogue around happiness and reinforces the notion that sharing meals is a global practice with profound implications for social connections and mental health.
Future Research Directions on Meal Sharing and Happiness
As the connection between meal sharing and happiness becomes increasingly clear, future research directions should delve deeper into this relationship. Investigating the causal dynamics—whether sharing meals genuinely increases happiness or whether happier individuals tend to engage in more meal sharing—can provide pivotal insights for both social science and public health. Understanding these nuances is essential for creating effective interventions that promote communal dining.
Additionally, future studies could focus on specific populations or contexts where shared meals may yield varied effects on happiness. By considering differences among age groups, cultural backgrounds, and social settings, researchers might uncover tailored approaches to enhance meal sharing practices. This exploration could significantly contribute to improving mental health outcomes, bolstering the argument for policy changes that prioritize community dining initiatives.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the correlation between shared meals and happiness?
Numerous studies, including findings from the World Happiness Report, indicate a strong correlation between shared meals and happiness. Individuals who frequently dine with others report greater life satisfaction and positive emotions, making meal sharing a reliable indicator of well-being.
How do shared meals impact mental health?
Shared meals can significantly enhance mental health by fostering social connections and reducing feelings of loneliness. Dining together promotes interactions that can lead to increased happiness, supporting the idea that mealtime gatherings contribute positively to emotional well-being.
What are the benefits of meal sharing for happiness?
Meal sharing cultivates deeper social bonds and improves overall happiness. Benefits include enhanced social support, improved mood through companionship, and the development of cherished memories, all contributing to higher levels of life satisfaction.
Do dining habits influence overall well-being?
Yes, dining habits have a profound impact on overall well-being. The frequency of shared meals plays a crucial role in determining happiness, with individuals who regularly share meals experiencing lower stress levels and higher life satisfaction.
What statistics support the link between shared meals and happiness?
Statistics from recent studies show that individuals who share meals are as likely to report high levels of happiness as those with significant income or stable jobs. For instance, the American Time Use Survey found a dramatic increase in solo dining, suggesting a potential decline in happiness linked to social isolation.
How can communal dining improve social connections?
Communal dining strengthens social connections by creating opportunities for meaningful conversations and relationship-building. Engaging in shared meals encourages community cohesion and helps combat feelings of isolation, ultimately enhancing happiness.
Are there specific dining habits that increase happiness?
Eating meals with family and friends regularly is crucial for increasing happiness. Moreover, participating in celebrations or cultural traditions centered around food can further enhance social bonds and emotional fulfillment.
How can shared meals serve as a policy intervention for mental health?
Encouraging shared meals can be an effective intervention for improving mental health and social well-being. By promoting community dining initiatives, policymakers can address rising levels of social isolation and enhance overall happiness within communities.
Can happiness levels be improved by changing dining patterns?
Yes, adjusting dining patterns to include more shared meals can lead to improved happiness levels. Emphasizing group dining experiences can foster social interactions that lead to enhanced emotional well-being.
What future research is needed on meal sharing and happiness?
Future research should focus on determining the causal relationship between meal sharing and happiness. Investigating whether increased communal dining directly elevates happiness levels, or if happier individuals tend to share more meals, will provide further insights into this important connection.
| Key Point | Details |
|---|---|
| Significance of Shared Meals | Shared meals are indicative of well-being, often outweighing income as a measure of happiness. |
| Trend in Meal Sharing | American dining habits show a 53% increase in solo meals since 2003, with 1 in 4 eating alone. |
| Demographics | This trend affects all ages, particularly young people, who are sharing fewer meals. |
| Correlation vs. Causation | While there is a correlation between shared meals and happiness, the causal relationship is still not fully understood. |
| Future Research | Researchers aim to investigate whether sharing meals increases happiness or if happier individuals are more likely to share meals. |
| Policy Implications | Encouraging shared meals can be an effective way to improve mental health and reduce social isolation. |
Summary
Shared meals and happiness are closely linked, as studies reveal that dining with others contributes significantly to overall well-being. The ability to share meals plays a crucial role in creating positive emotions and a sense of community, which are essential for happiness. As society faces increasing rates of social isolation, promoting shared meals can serve as a valuable strategy to enhance social connections and improve mental health. Ultimately, making the effort to bring people together over a meal can lead to greater life satisfaction and a happier society.