Prion disease treatment is on the forefront of groundbreaking research, providing a beacon of hope for those affected by these rare but devastating neurodegenerative disorders. Scientists are making strides in understanding how misfolded proteins cause conditions like Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease and fatal familial insomnia, paving the way for innovative therapies. Recent studies have explored gene editing therapy as a promising approach to target the genetic roots of these diseases, potentially altering the progression of protein misfolding in the brain. The journey of patient-scientists like Sonia Vallabh and Eric Minikel, who deeply understand the personal stakes, underscores the urgency and significance of this research. As we delve deeper into prion disease research, the development of effective treatments is an ambitious yet achievable goal that could transform lives.
The exploration of effective treatments for prion diseases represents a critical area in medical science, specifically focusing on rare neurodegenerative conditions characterized by abnormal protein folding. Alternative terms like transmissible spongiform encephalopathies (TSEs) or prion disorders highlight the complex nature of these diseases, which include well-known examples such as Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. With ongoing advancements in gene editing technology and therapies aimed at addressing the underlying genetic mutations, the future looks promising. These efforts are accompanied by the dedication of patient-scientists who face these challenges personally, driving the research forward with unparalleled motivation and insights. The intersection of cutting-edge science and real-life experiences may well lead to significant breakthroughs in the fight against these fatal disorders.
Understanding Prion Diseases and Their Impact
Prion diseases are a group of rare and invariably fatal neurodegenerative disorders that are caused by misfolded proteins in the brain. Among the most notorious of these are Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease and fatal familial insomnia. These conditions can lead to severe neurological symptoms, including memory loss, impaired cognitive function, and ataxia, ultimately resulting in death. The complex nature of prion diseases has been a significant challenge for researchers, as their pathophysiology involves not just genetic factors but also sporadic occurrences where wild-type prion proteins fold abnormally, leading to the accumulation of toxic aggregates in the brain.
The impact of prion diseases is not limited solely to the affected individuals; it extends to families and caregivers, often leading to profound emotional and psychological stress. For instance, in the case of fatal familial insomnia, patients face a debilitating decline in quality of life, with symptoms that can include insomnia, hallucinations, and eventual loss of motor control. The urgent need for effective treatments is underscored by the personal stories of many caregivers and scientists, including those directly afflicted by these diseases, who have transformed their grief into a mission to find viable therapies.
Advancements in Prion Disease Treatment
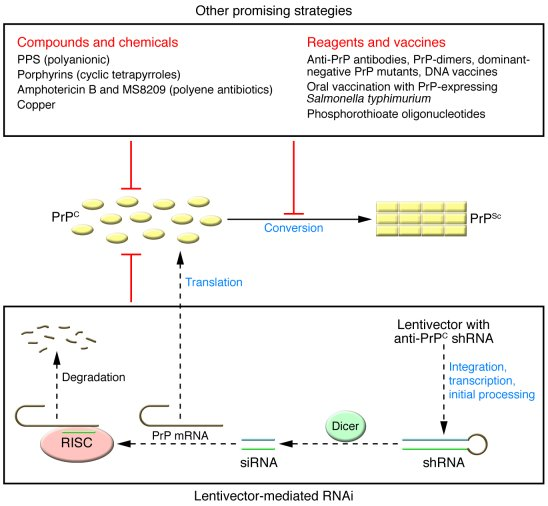
Recent advancements in prion disease treatment have sparked optimism in the scientific community. Researchers at institutions like the Broad Institute of MIT and Harvard have made significant strides, particularly with the development of gene editing therapies aimed at disrupting the production of harmful prion proteins. This groundbreaking research employs single-base editing technology that can effectively reduce prion protein levels by altering a single base pair in the prion protein gene. Such interventions have shown the potential to increase the lifespan of experimental models dramatically, showcasing a promising pathway toward human treatments.
Although these findings are encouraging, researchers caution that there is a lengthy road ahead before human trials can commence. The complexity of prion disease treatment necessitates rigorous testing and refinement of the gene-editing techniques to ensure safety and efficacy in humans. Adapting this technology also involves addressing challenges such as the delivery mechanisms to adequately target affected cells and minimize off-target effects, ensuring that the therapeutic benefits outweigh any potential risks.
The Role of Patient-Scientists in Research
The involvement of patient-scientists like Sonia Vallabh and Eric Minikel in prion disease research has added a profoundly personal dimension to scientific inquiry. Their journey began with the tragic loss of Vallabh’s mother to fatal familial insomnia, followed by her own diagnosis. This unique perspective not only drives their research efforts but also fosters collaboration within the broader scientific community, highlighting the importance of empathy and personal investment in tackling complex diseases.
Patient-scientists bring invaluable insights to research teams, offering a perspective that transcends traditional academic boundaries. Their experiences fuel motivation among their peers, as seen in Vallabh and Minikel’s collaboration with David Liu’s research group. This collaborative spirit enhances the research process, inspiring collective and innovative solutions to the challenges presented by prion diseases. Such engagement illustrates the potential for patient-led initiatives to impact the pace and direction of scientific advancements in effective prion disease treatments.
Gene Editing Therapy: A Beacon of Hope
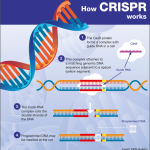
Gene editing therapy represents a significant breakthrough in the field of prion disease treatment. Utilizing tools like CRISPR, researchers have begun to explore ways to correct genetic mutations that lead to the production of misfolded proteins. This innovative approach aims not only to mitigate the symptoms of prion diseases like Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease but also to address the underlying genetic factors that contribute to these conditions. The ability to edit genes offers a promising avenue for developing targeted therapies that could alter the disease course for those affected.
While optimism surrounds gene editing therapy, the path to clinical application is riddled with hurdles that need to be addressed. Scientists must navigate regulatory environments, ethical considerations, and safety concerns associated with editing human genomes. As researchers refine these techniques through preclinical studies in mouse models, the possibility of translating findings into effective treatments for humans becomes more tangible. Continued investment in prion disease research is essential for unlocking the potential of gene editing therapies and bringing new hope to patients and their families.
Challenges of Researching Prion Proteins
Researching prion proteins is fraught with challenges that stem from their unique properties. Prions are infectious agents that can transmit their misfolded shape, making it difficult to study them in laboratory settings without posing risks to researchers and the public. The accidental exposure incidents, such as the tragic case in France where a researcher died from prion disease, have led to stringent regulations governing prion research, further complicating efforts to understand and develop treatments for these disorders.
Moreover, the nature of prion diseases demands an interdisciplinary approach that combines genetics, neurology, and protein science. Researchers must collaborate across fields and institutions to share insights and techniques, finding innovative solutions to the scientific roadblocks they face. This necessity for collaboration is highlighted in current research efforts, where teams are coming together to address the intricate challenges posed by prion proteins and pursue breakthroughs that could lead to effective therapeutics.
The Future of Prion Disease Research
The future of prion disease research looks promising, thanks in large part to advancements in biotechnology and a renewed focus on gene editing techniques. As scientists deepen their understanding of the mechanisms behind prion diseases, they are laying the groundwork for transformative treatment options. The research community is enthusiastic about the prospect of developing clinical applications that could soon emerge from laboratory findings, allowing for targeted treatments that modify the disease process at a molecular level.
However, the road ahead is not devoid of obstacles. Researchers must continue to refine their methods to ensure that these approaches can be safely and effectively translated into human therapies. Ongoing clinical trials will be crucial in validating the efficacy of novel treatment strategies and ensuring that they are both safe and beneficial for patients. With the persistent efforts of dedicated scientists and the engagement of patient advocates, there is hope that breakthroughs in prion disease treatment will lead to significant advancements in alleviating the suffering caused by these fatal disorders.
Collaboration in Prion Disease Research
Collaboration is essential in the field of prion disease research, as no single entity possesses all the resources and expertise required to tackle such a complex challenge. By working together, researchers can combine their knowledge on protein misfolding, genetic manipulation, and clinical applications to enhance the quality and effectiveness of their investigations. Collaborative initiatives often yield innovative strategies that address multifaceted aspects of prion diseases, improving the chances of developing viable treatment options.
Successful partnerships can take various forms, including academia-industry collaborations, interdisciplinary research consortia, and patient-researcher alliances. These collaborative frameworks not only foster a sharing of ideas but also allow for the rapid exchange of information necessary to address pressing research questions. Furthermore, collaboration empowers researchers to navigate regulatory hurdles more efficiently, pooling resources and expertise to advance the timeline of research and improve outcomes for patients suffering from prion diseases.
Patient Advocacy in Prion Disease Research
Patient advocacy has emerged as a crucial element in prion disease research, bringing attention to the urgent need for effective treatments and encouraging the scientific community to prioritize these often-overlooked conditions. Individuals and families affected by prion diseases have become vocal proponents for research funding and innovation, emphasizing the impact that these disorders have on their lives. Their stories humanize the scientific endeavor and remind researchers of the ultimate goal: to alleviate suffering and improve patient outcomes.
Advocacy efforts have led to increased awareness and investment in prion disease research, fostering a culture where the voices of patients are heard and integrated into the research agenda. Patient advocates often collaborate with researchers to define priorities, ensuring that research efforts are aligned with the needs and hopes of those impacted by prion diseases. This symbiosis between advocacy and research is vital in creating a robust framework for developing effective therapies that have a meaningful impact on patients’ lives.
Current Trends in Prion Disease Research
Current trends in prion disease research indicate a burgeoning interest in the application of advanced technologies and novel therapeutic strategies. Emerging techniques in molecular biology, such as gene editing and RNA-based therapies, are being actively explored to not only understand the underlying mechanisms of prion diseases but also develop treatments that could mitigate their effects. There is also an increasing emphasis on personalized medicine, allowing for tailored approaches that consider the unique genetic profiles of patients with hereditary forms of prion disease.
Moreover, interdisciplinary research teams are becoming more commonplace, as experts from diverse fields collaborate to tackle the challenges posed by prion diseases. This integration of various scientific disciplines fosters innovation and accelerates the pace of discovery. By leveraging advancements in biotechnology, genetics, and neurobiology, researchers are positioned to unlock new avenues for therapeutic interventions that may ultimately lead to effective treatments for prion diseases.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the latest advancements in prion disease treatment through gene editing therapy?
Recent research has showcased promising advancements in prion disease treatment, particularly through gene editing therapy. Scientists have managed to successfully reduce harmful prion protein levels in the brains of laboratory mice by 50%, thanks to a unique base editing technology. This breakthrough not only extends the mice’s lifespans significantly but also paves the way for potential future treatments for conditions like Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease and fatal familial insomnia.
How does gene editing therapy target protein misfolding in prion diseases?
Gene editing therapy targets protein misfolding in prion diseases by directly altering the genetic instructions responsible for producing harmful proteins. This approach uses techniques such as single base editing, which modifies the specific genes associated with prion diseases. As a result, researchers have observed a notable decrease in the production of these misfolded proteins, which are essentially the hallmark of prion disorders.
What is the significance of the recent research in prion disease treatment for patients with fatal familial insomnia?
The recent research in prion disease treatment holds considerable significance for patients with fatal familial insomnia. Since this condition is genetically linked to prion protein mutations, the development of gene editing therapy provides hope for effectively targeting the root cause of the disease. Patient-scientists, such as Sonia Vallabh, directly involved in the research, emphasize the personal stakes in finding a viable treatment through these innovative methods.
How does prion disease research contribute to the development of potential therapies?
Prion disease research is crucial for the development of potential therapies as it sheds light on the mechanisms by which prion diseases, including Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease, affect the brain. By understanding the misfolding of proteins and how genetic interventions can mitigate these effects, researchers are better equipped to create targeted treatments that can alter the progression of these fatal disorders.
Will gene editing therapy be available for human trials in treating prion diseases?
While current research indicates that gene editing therapy shows promise for treating prion diseases in animal models, human trials remain several years away. Researchers are diligently working on refining the techniques and ensuring safety to prepare for eventual testing in human subjects. The optimism surrounding these breakthroughs inspires hope for those diagnosed with conditions like fatal familial insomnia and Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease.
| Key Points | Details |
|---|---|
| Research Focus | Investigation of gene-editing therapy for prion diseases. |
| Definition of Prion Diseases | Rare, fatal disorders caused by misfolded proteins in the brain. |
| Scientific Breakthrough | Gene editing can reduce harmful protein presence by 50%, extending mice lifespans by 52%. |
| Personal Connection | Sonia Vallabh, a researcher, has tested positive for fatal familial insomnia. |
| Collaboration | Researchers have collaborated with various institutes and centers to advance treatment. |
| Next Steps | Research on base editing refinement and human trials are anticipated but may take years. |
Summary
Prion disease treatment is advancing with recent discoveries in gene-editing therapies that show potential for slowing the progression of these fatal conditions. Researchers, including patient-scientists like Sonia Vallabh, are dedicated to transforming personal experiences with prion illnesses into scientific progress, working toward innovative therapies. As they refine these approaches, the hope for translating laboratory successes into effective treatments for human patients grows stronger, although several significant hurdles remain before clinical trials can commence.