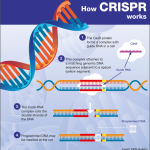
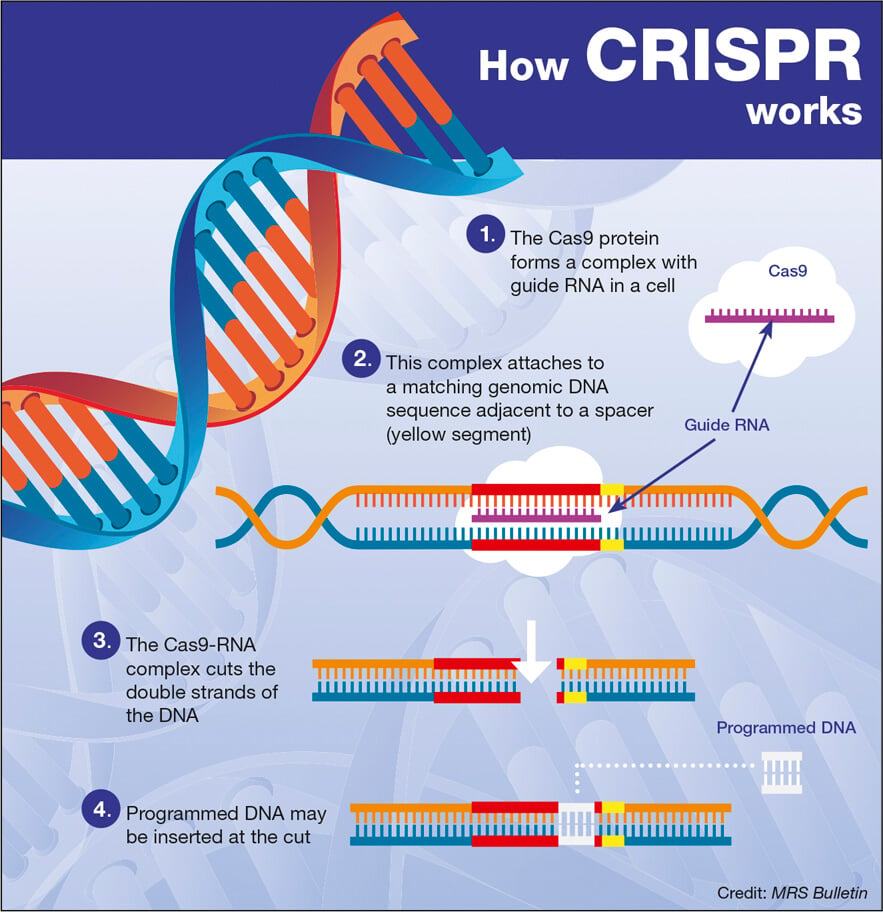
CRISPR gene editing is revolutionizing the medical landscape, offering unprecedented possibilities for the treatment of genetic diseases such as sickle cell anemia. This cutting-edge CRISPR technology enables scientists to alter the DNA sequences in a highly precise manner, sparking discussions around gene therapy’s potential to eradicate genetic disorders. However, as researchers explore these advancements, the ethical implications of gene editing, especially regarding gene editing ethics, are increasingly coming under scrutiny. Consideration of health justice becomes vital as these treatments raise questions about accessibility and fairness in healthcare. As we delve into the promise of curing diseases through gene manipulation, we must also confront the moral responsibilities intertwined with these scientific breakthroughs.
Gene modification techniques have gained immense attention, especially when discussing the implications of altering human genetics for health improvements. With the advent of advanced genetic engineering tools, scientists are exploring potential treatments for conditions like sickle cell disease, bringing new hope to many families. Yet, alongside these innovations, significant concerns related to genetic alteration ethics emerge, particularly around issues of equity and access to therapies. The concept of health equity takes center stage as these powerful technologies become available, often highlighting disparities in who can benefit from them. As society grapples with these advancements, the ongoing dialogue about the responsibilities of gene therapy becomes crucial in ensuring fair access to medical advancements.
Understanding CRISPR Gene Editing: A Breakthrough in Medicine
CRISPR gene editing represents a revolutionary advancement in the field of genetics, offering unprecedented capabilities to modify and correct genetic disorders. This technology allows scientists to make precise changes to the DNA within living organisms, which can lead to effective treatments for various genetic conditions, such as sickle cell anemia. By utilizing CRISPR technology, researchers are not only able to target specific genes associated with debilitating diseases but also potentially eradicate them before they can affect an individual’s health, thus transforming the landscape of modern medicine.
However, the implementation of CRISPR gene editing raises significant ethical and moral questions. As we gain the ability to edit the human genome, we must confront the implications of altering human traits, including intelligence and physical characteristics. This opens a Pandora’s box of societal issues surrounding equity in health care, access to genetic therapies, and the long-term impacts on genetic diversity. Therefore, it is crucial to approach gene editing not only with scientific enthusiasm but also with a deep commitment to ethical considerations.
The Ethical Landscape of Gene Editing
Gene editing ethics is a crucial topic as we explore the capabilities of technologies like CRISPR. The questions surrounding the appropriateness of gene editing extend beyond the science itself; they delve into philosophical realms about what it means to be human. Should we have the right to ‘design’ our offspring or remove traits that we perceive as undesirable? Moreover, who gets to make those decisions, especially in instances where conditions like Down syndrome—compatible with life—are concerned? The growing debates focus on ensuring that we do not encroach on the personal choices and existences of individuals who identify with such conditions.
Additionally, the rise of gene editing presents a stark contrast between those who have access to advanced therapies and those who do not. As highlighted by healthcare equity advocates, the costs associated with CRISPR treatments, such as the estimated $2.2 million for sickle cell disease, poses a significant barrier. If only a fraction of society can afford these innovations, we risk deepening existing health disparities. Ethical frameworks must be established to govern not only the application of gene editing technologies but also the equitable distribution of their benefits across diverse populations.
Health Justice: Access and Equity in Gene Therapy
Health justice emerges as a vital consideration in the evolution of gene therapies, particularly those enabled by CRISPR technology. As potential treatments for severe genetic conditions like sickle cell anemia become available, questions surrounding who can access these therapies loom large. The staggering costs serve as a barrier for many, raising the issue of fairness in medical treatment and the responsibility of healthcare systems to provide equitable solutions. Ensuring that all patients have access to cutting-edge treatments remains a pressing concern amidst the promise of scientific advancement.
Moreover, health justice isn’t simply about access but also about the ethical considerations that arise when prioritizing certain conditions over others. As researchers and policy-makers define which genetic disorders warrant intervention, they must grapple with deeply entrenched societal biases that influence these decisions. The disparities in health outcomes experienced by marginalized communities call for a robust dialogue around health equity and the moral implications of genetic technology. It’s crucial that we advocate for inclusivity in gene therapy discussions, ensuring that all voices, particularly those of marginalized groups, play a significant role in shaping health policies.
The Future of CRISPR Technology: Revolution or Risk?
The future of CRISPR technology holds immense potential, promising breakthroughs that could reshape the landscape of healthcare. As scientists continue to explore its applications, we stand at the brink of innovations that could one day cure genetic disorders and enhance our understanding of human biology. The ability to edit genes effectively opens up pathways for personalized medicine, enabling tailored therapies that align with individual genetic profiles, ultimately leading to improved health outcomes and quality of life.
Nonetheless, the advancement of CRISPR technology also necessitates rigorous scrutiny and oversight. The ethical ramifications of gene editing require a careful balance between scientific progress and the potential for misuse. As discussed in various forums, the possibility of creating ‘designer babies’ or genetically modifying traits raises profound moral dilemmas that society must navigate. Establishing comprehensive regulatory frameworks will be essential to manage these technologies responsibly, ensuring that the benefits of CRISPR are harnessed for the greater good while minimizing the risks associated with its application.
Sickle Cell Anemia Treatment: The Promise and the Questions
Sickle cell anemia treatment using CRISPR technology presents a remarkable opportunity for those suffering from this debilitating condition. By targeting the mutated genes responsible for sickle cell disease, researchers have made significant strides toward developing curative therapies that offer hope for many patients. The ability to edit somatic cells allows for the direct correction of the underlying genetic defect, potentially transforming the lives of individuals who have long endured this painful disorder.
However, the application of CRISPR in treating sickle cell anemia is not without controversy. The high costs associated with these innovative therapies raise concerns about access and affordability, as many families may be unable to bear the financial burden of such treatments. Additionally, ongoing discussions about the ethical implications of gene editing underscore the need for transparency and consent in the research process. It is vital to engage affected communities in these conversations to ensure that treatment strategies are equitable and respect the dignity of all individuals.
Balancing Innovation and Ethics in Genetic Research
As advancements in genetic research continue at a rapid pace, finding the equilibrium between innovation and ethics becomes increasingly critical. The rapid rise of CRISPR technology has ushered in a new era of possibilities in medicine, but it has also illuminated the need for a thoughtful approach to its use. Discussions surrounding gene editing ethics highlight the necessity of establishing guidelines that protect both individual rights and the integrity of human genetics.
Innovators in the field must prioritize ethical considerations alongside their scientific pursuits, recognizing the potential consequences of their work on society. This means engaging with ethicists, policymakers, and community stakeholders to create cohesive frameworks that govern the use of gene-editing technologies. By fostering an environment where ethical standards guide scientific exploration, we can harness the potential of CRISPR while safeguarding against unintended consequences and ensuring that all communities benefit from these innovations.
Implications of Germline Editing: A Deeper Look
The implications of germline editing form a complex tapestry of potential benefits and ethical dilemmas. Unlike somatic cell editing, which impacts only the treated individual, germline editing involves altering the DNA passed down to future generations. This capability could herald significant advancements in preventing hereditary diseases but also raises profound ethical questions about the extent of human agency in genetic inheritance. Should we, as a society, decide which traits are desirable or undesirable, and who will have the authority to make these decisions?
The debates surrounding germline editing spark concern about eugenics and the societal consequences of ‘enhancing’ certain human traits. Such discussions emphasize the need for global dialogue on regulatory practices that will govern the use of this powerful technology. As we delve deeper into the realm of germline modifications, the implications extend beyond science, touching on cultural, social, and ethical dimensions that must be carefully navigated to prevent misuse and ensure a just application of these scientific advancements.
The Role of Oversight in Gene Editing Research
The role of oversight in gene editing research is crucial in ensuring the responsible development and application of CRISPR technology. As the field rapidly evolves, creating effective regulatory frameworks becomes indispensable to monitor research and its applications. Oversight committees and regulatory bodies must be established to evaluate research proposals critically, considering not only the scientific merit but also the potential ethical implications and societal impact of gene editing innovations.
Effective oversight involves a collaborative effort among scientists, ethicists, and policymakers to draft guidelines that prioritize safety, efficacy, and moral responsibility. This approach may include establishing clear criteria for which conditions warrant gene editing interventions while safeguarding against exploitation and ensuring equitable access. As gene editing technology advances, robust oversight mechanisms will be pivotal in fostering public trust, protecting human rights, and steering research towards paths that benefit society as a whole.
Engaging Communities in Gene Editing Conversations
Engaging communities in discussions about gene editing technology is essential to fostering a comprehensive understanding of its implications. As CRISPR technology evolves, the voices of those most affected by genetic conditions, including patients and their families, must be included in the dialogue surrounding gene editing. By incorporating diverse perspectives, we can ensure that ethical considerations reflect the values and needs of the communities most impacted by these advancements.
Moreover, public engagement initiatives can educate and empower individuals about the complexities of gene editing, offering a platform for concern, curiosity, and collaboration. Such outreach may involve workshops, webinars, and forums that encourage open dialogue between stakeholders, including scientists, ethicists, and community representatives. This engagement can lead to more equitable and inclusive decision-making processes, ultimately shaping policies that truly reflect the collective interests of society.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the ethical implications of using CRISPR gene editing technology?
The ethical implications of CRISPR gene editing technology are significant. These include questions about the morality of altering human genes, the consent of future generations, and the fairness of access to such treatments. As noted by experts, using CRISPR for diseases like sickle cell anemia raises concerns about health equity, especially regarding who benefits from these advancements and who decides what conditions are worthy of treatment.
How is CRISPR technology being used in the treatment of sickle cell anemia?
CRISPR technology enables precise editing of genes involved in sickle cell anemia. By manipulating somatic cells, scientists can effectively remove the genetic mutations causing the disease, potentially curing patients. Germline editing could also prevent sickle cell from developing in embryos. However, the use of CRISPR in this context raises ethical questions about gene manipulation and the potential for unforeseen consequences.
What role does health justice play in discussions about CRISPR gene editing?
Health justice is a critical consideration in discussions about CRISPR gene editing, especially regarding the accessibility of gene therapies. As highlighted by experts, innovations in gene editing can exacerbate disparities between those who can afford such treatments and marginalized communities. It prompts a broader dialogue about how to ensure that all individuals have equitable access to CRISPR technology and its benefits.
Are there any risks associated with CRISPR gene editing technology?
Yes, while CRISPR technology holds promise for gene editing, it also presents several risks. Potential risks include unintended genetic changes, ethical dilemmas regarding the modification of human traits, and global disparities in regulation. Experts caution that while certain applications appear beneficial, the long-term consequences of editing genes may lead to complex health issues, as genes interact in multifaceted ways.
How do societal values influence the debate on CRISPR gene editing ethics?
Societal values greatly influence the debate on CRISPR gene editing ethics. Perspectives on what constitutes a ‘normal’ or ‘desirable’ trait vary widely, impacting decisions about which genetic conditions should be treated. The ethical discourse often reflects deeper societal beliefs about disability, diversity, and the nature of human variation, making it essential to incorporate diverse voices and values into the conversation surrounding CRISPR technology.
| Key Point | Description |
|---|---|
| Ethical Questions | CRISPR raises questions about the morality of altering human genes and the implications of such changes. |
| Sickle Cell Treatment | CRISPR can potentially cure sickle cell anemia but raises questions about who benefits and who should pay. |
| Germline vs Somatic Editing | CRISPR allows for editing both somatic and germline genes, with different implications for future generations. |
| Health Equity | The high costs of gene modifications raise issues of accessibility and fairness in healthcare. |
| Parental Decision-Making | Discussions around whether parents should decide genetic traits for their children are ongoing. |
| Oversight and Regulation | Concerns about the lack of global regulations for gene editing raise fears of misuse. |
| Unintended Consequences | Altering genes may have complex implications due to the interconnectedness of genetic factors. |
Summary
CRISPR Gene Editing represents a groundbreaking advancement in the field of genetics, providing the potential to treat and cure genetic disorders. However, as explored in recent discussions, the technology also surfaces profound ethical dilemmas and societal implications. The ability to edit genes not only prompts questions about health equity and parental rights but also emphasizes the need for robust regulatory frameworks to manage these powerful tools responsibly. The ongoing debate surrounding CRISPR highlights the necessity of balancing innovation with ethical considerations to ensure that the benefits of gene editing are equitably distributed.