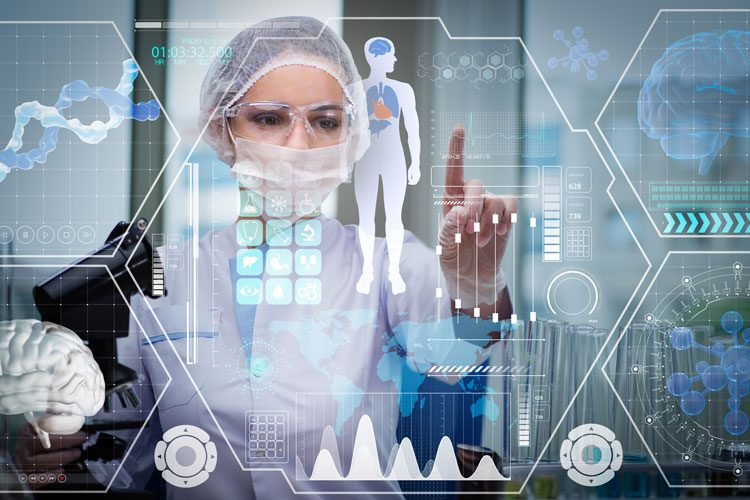
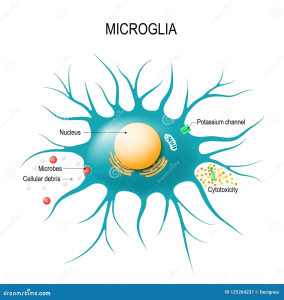
Artificial intelligence in medicine is revolutionizing how healthcare is delivered, ensuring that patients receive quicker and more accurate diagnoses. With advancements in artificial intelligence healthcare, tools such as large language models are reshaping the medical landscape by facilitating enhanced doctor-patient interactions and improving clinical decision-making. The AI medical benefits are significant as they reduce administrative burdens, allowing healthcare professionals to focus more on patient care. Innovations like AI-driven apps can instantly analyze vast medical literature, providing tailored information and recommendations during consultations. As we look toward the future of healthcare AI, we can anticipate a more efficient and compassionate system that elevates the quality of care delivered.
The integration of smart technologies in healthcare, particularly through artificial intelligence applications, is changing the game for how medical professionals engage with patients. These intelligent systems are enhancing clinician capabilities, enabling faster access to critical information and driving more informed treatment decisions. The evolving doctor-patient relationship is further transformed as AI tools provide real-time feedback and support, empowering practitioners in their practice. As we explore the possibilities of AI in medical settings, the prospect of harnessing these innovations signals a promising shift toward a more patient-centered approach in the evolving healthcare landscape. Significantly, the collaborative potential between human expertise and cutting-edge technology holds the key to unlocking new avenues in medical excellence.
The Growing Role of AI in Medicine
Artificial intelligence (AI) is rapidly transforming the landscape of healthcare, showcasing capabilities that were once thought to be the stuff of science fiction. Innovations like large language models have created new opportunities to enhance the efficiency of medical practitioners. These AI-driven systems can analyze vast datasets and offer insights that support clinical decision-making, thus improving patient outcomes. For instance, the ability to access extensive medical literature in real-time allows healthcare providers to make informed decisions that are aligned with the latest evidence-based practices.
Moreover, the integration of AI into healthcare has the potential to alleviate the burdens faced by clinicians. Tasks such as documentation, scheduling, and even initial patient assessments can be streamlined through AI applications, enabling doctors to focus more on patient care rather than administrative duties. The promise of AI in medicine extends beyond operational efficiency; it heralds a future where healthcare can be both personalized and scalable.
Enhancing Doctor-Patient Relationships with AI
The introduction of AI tools into healthcare promises to significantly alter the doctor-patient relationship for the better. With AI providing real-time second opinions and comprehensive data analyses, patients can expect more insightful discussions during their consultations. The dynamic of having an AI assistant means that physicians can rely on data-driven insights that enrich patient interactions, fostering a more engaged and informed dialogue.
This shift not only empowers doctors but also enhances the patient experience by making medical care more accessible and understandable. For instance, systems that interpret symptoms and suggest possible diagnoses allow patients to participate in their healthcare journey actively. By providing patients with accurate information and treatment options derived from AI capabilities, the value of human empathy and support can be further centered in clinical settings.
AI Medical Benefits: Addressing Patient Safety
AI in medicine presents substantial benefits, particularly in improving patient safety. Advanced algorithms can analyze clinical data to identify potential risks and adverse events more accurately than traditional methods. For example, AI can alert healthcare providers to possible medication interactions or highlight abnormal lab results before they become critical, thereby facilitating timely interventions.
The focus on safety extends to chronic disease management, where predictive analytics can help in monitoring patients more effectively. By continuously analyzing health data, AI can assist healthcare teams in anticipating issues before they escalate, ultimately leading to better management of complex health conditions. This proactive approach greatly reduces the risk of avoidable complications, ensuring that patient care is both safe and efficient.
The Impact of Large Language Models on Healthcare
Large language models (LLMs) have revolutionized the way medical professionals access information and make decisions. These sophisticated AI tools can understand and generate human-like text, allowing them to synthesize vast amounts of medical literature quickly. Physicians can utilize these models for tasks ranging from drafting patient notes to conducting detailed literature reviews, drastically cutting down the time required for research and improving the quality of care provided.
Moreover, the versatility of LLMs means they can be adapted for various applications within healthcare, from personalized medicine to enhancing medical education. As future physicians harness these technologies in their training, they will be better prepared to utilize AI tools effectively in clinical practice, fostering a generation of healthcare providers who can leverage technology to advance patient care beyond current capabilities.
The Future of Healthcare AI: Navigating Challenges and Opportunities
As the field of AI in medicine evolves, it faces a unique set of challenges that need addressing to fully realize its potential. Issues such as algorithmic bias, data privacy, and the need for regulatory frameworks are critical in determining how these technologies will be integrated into healthcare systems. Experts highlight the importance of ensuring that AI technologies are trained on diverse datasets to prevent the perpetuation of existing health disparities, particularly among marginalized populations.
Conversely, the opportunities presented by this burgeoning field are equally significant. By investing in robust AI solutions that prioritize safety, efficacy, and inclusiveness, healthcare systems can profoundly enhance patient outcomes and operational efficiency. Embracing a holistic view of AI as a collaborative partner rather than a replacement for human clinicians will be crucial in shaping a future where healthcare is equitable and innovation-driven.
AI’s Transformational Impact on Medical Education
The integration of AI in medical education is reshaping how future physicians are trained. With AI tools being introduced into curricula, students can expect to learn in environments enriched by technology that emphasizes critical thinking and problem-solving over rote memorization. For example, AI can simulate complex patient scenarios where students learn to diagnose and create treatment plans, thus better preparing them for real-world situations.
Additionally, the incorporation of AI into educational systems allows for more individualized learning experiences. As students interact with AI-driven systems, they can receive personalized feedback and support tailored to their learning styles. This technological advancement is expected to produce graduates who are not only proficient in medical knowledge but are also adept at leveraging AI to enhance future patient care.
AI in Healthcare: Mitigating Burnout for Physicians
One of the pressing issues in today’s healthcare environment is physician burnout, which has significant implications for both practitioner well-being and patient care quality. AI tools offer promising solutions by automating routine tasks, thereby reducing the administrative workload on healthcare providers. For instance, ambient documentation technologies that can summarize patient visits in real-time allow doctors to engage with their patients without the distraction of note-taking.
Decreasing the clerical burden on healthcare professionals could restore a sense of purpose and satisfaction to their roles, ultimately improving the quality of care that patients receive. By alleviating some of the stress commonly associated with medical practices, AI has the potential to foster a healthier work-life balance for physicians and empower them to focus more on what they were trained to do: care for patients.
Tackling Data Biases in AI Healthcare Solutions
As AI systems become ubiquitous in healthcare, the issue of data bias poses a significant challenge. Many AI models utilize datasets that reflect historical inequalities in the health system, resulting in tools that may not serve all patient populations equally. Addressing these biases is critical to ensuring that AI in medicine benefits everyone and does not exacerbate existing health disparities.
To combat data bias, it is crucial for medical researchers and developers to prioritize diversity in both the dataset and the clinical trials that inform AI training. By doing so, they can create more accurate and reliable AI tools that can address the needs of various patient demographics. This approach ultimately supports a more equitable healthcare system where AI technologies work effectively across diverse backgrounds.
Building a Collaborative Future: Humans and AI in Medicine
The future of AI in medicine is not about replacing healthcare professionals but rather enhancing their capabilities. A collaborative approach where human judgment and AI technology work hand in hand can lead to unprecedented improvements in patient care. This partnership ensures that while AI handles data-heavy tasks and algorithms, healthcare providers can focus on the intricate art of patient care.
Encouraging ongoing collaboration between AI systems and medical experts could lead to innovative solutions that better meet the complex demands of healthcare today. This development not only benefits patient outcomes but also cultivates an environment where healthcare professionals feel supported and empowered to utilize technology fearlessly.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the key benefits of implementing artificial intelligence in healthcare?
Artificial intelligence (AI) in healthcare offers numerous benefits, including enhancing diagnostic accuracy, improving patient outcomes, and streamlining administrative processes. AI medical benefits also extend to reducing workload burdens on clinicians, allowing for more personalized patient care and enabling quicker access to medical information. With AI tools, healthcare professionals can efficiently analyze vast amounts of data, leading to informed decision-making and optimized treatment plans.
How do large language models impact the doctor-patient relationship?
Large language models (LLMs) in medicine are transforming the doctor-patient relationship by providing instant second opinions and facilitating better communication. These AI tools enhance the quality of interactions, allowing doctors to focus on patient engagement rather than administrative tasks. With AI assistance, patients can receive more timely and accurate responses to their questions, fostering a collaborative environment that prioritizes their healthcare needs.
What does the future of healthcare AI look like?
The future of healthcare AI is poised for revolutionary changes, with advancements in technology promising to improve efficiency and patient care. Experts predict that the integration of AI will deepen the understanding of complex medical conditions and enhance personalized treatment approaches. As AI becomes more prevalent, it is expected to augment the capabilities of healthcare professionals, reshaping medical training, research, and practice to better meet the needs of patients.
How do biases in AI affect healthcare outcomes?
Biases in AI can significantly affect healthcare outcomes by perpetuating disparities in treatment and access. For instance, if the data used to train AI models reflect existing societal biases, this can lead to inequitable care for disadvantaged groups. Addressing these biases is crucial for ensuring that artificial intelligence in healthcare leads to fair and effective patient interactions, reducing the risk of reinforcing existing health disparities.
In what ways can AI enhance medical education?
AI has the potential to enhance medical education by facilitating personalized learning experiences and simulating clinical scenarios. By utilizing AI tools, students can access vast databases of medical knowledge, practice on virtual patients, and receive real-time feedback. This innovative approach equips future healthcare providers with the skills needed to navigate complex medical landscapes and utilize AI effectively in their practice.
| Aspect | Key Points |
|---|---|
| AI in Medicine | Experts believe AI can significantly reduce human suffering in healthcare. |
| Transformation of Medical Practice | AI tools, particularly large language models, are revolutionizing doctor-patient interactions and administrative tasks, improving efficiency. |
| Concerns and Challenges | Bias in data sets and ‘hallucination’ of facts pose risks for AI in medicine, threatening equitable care. |
| Diversity and Bias mitigation | It is crucial to diversify training data to avoid perpetuating inequalities in healthcare. |
| Future Perspectives | To maximize benefits from AI, a balance between technology and human oversight is critical in medical training and practice. |
| Potential for Enhanced Learning | AI can aid medical education by providing immediate access to vast information and reducing paperwork. |
Summary
AI in medicine presents an unprecedented opportunity to enhance patient care and streamline healthcare practices. As we adapt to the integration of artificial intelligence, particularly large language models, it is essential to address biases and ethical concerns to ensure equitable access and accuracy in healthcare delivery. By harnessing the capabilities of AI, we can aim for a future where medical professionals are not only equipped with powerful tools for diagnosis and treatment but are also encouraged to cultivate critical thinking and empathetic patient interactions.