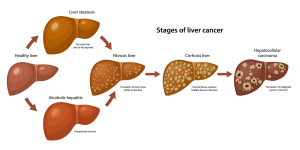
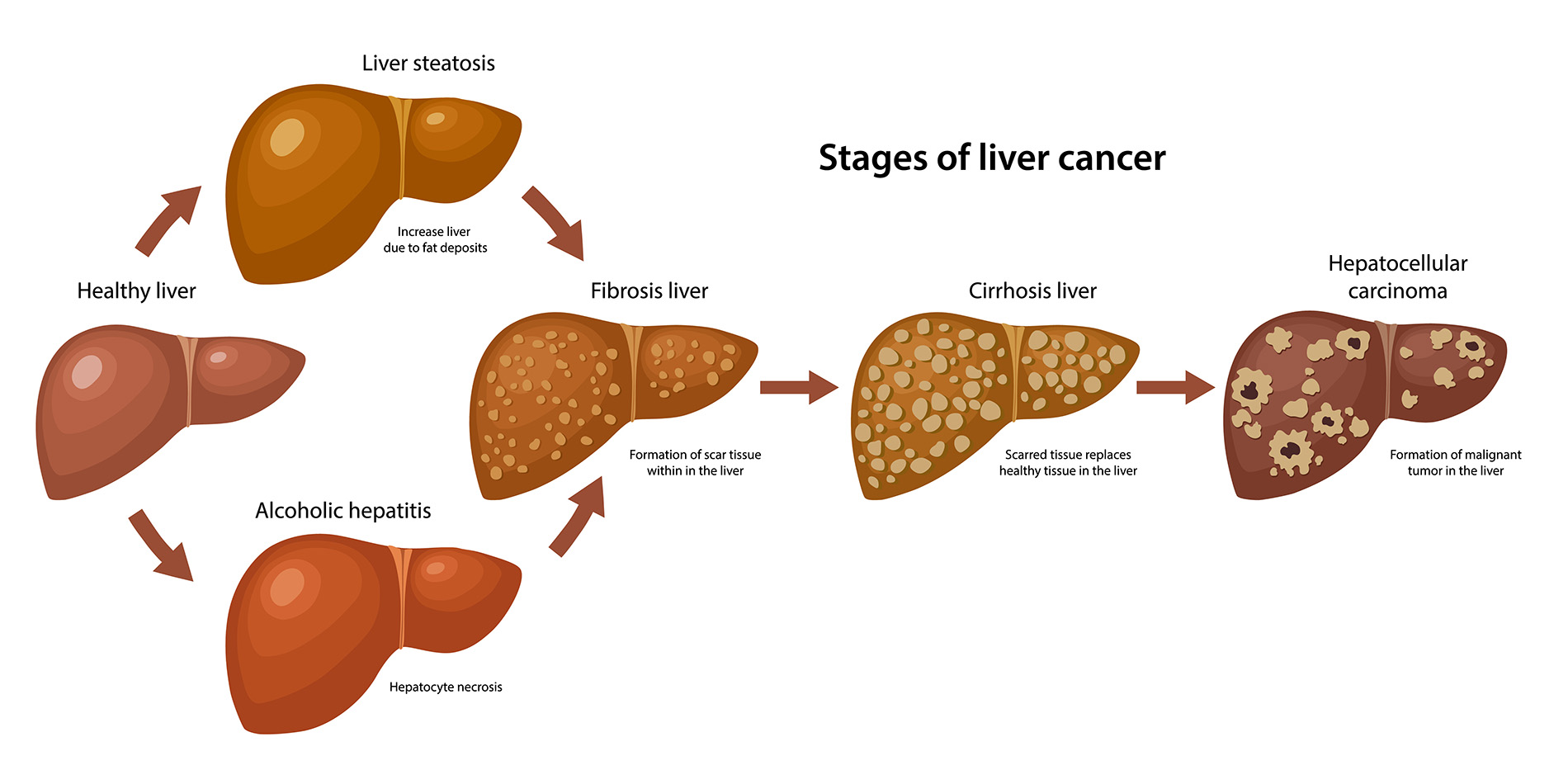
Liver cancer bile imbalance is emerging as a critical factor in the development of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), the most prevalent form of liver cancer. Recent research has uncovered the intricate relationship between bile acid metabolism and liver disease progression, highlighting how disruptions in bile production can amplify liver inflammation and fibrosis. This imbalance is often tied to anomalies in vital pathways, such as the Hippo/YAP signaling mechanism, which plays a significant role in tumor formation. Furthermore, a key bile acid sensor dubbed FXR is pivotal in maintaining bile homeostasis, and its dysfunction can exacerbate cancer risk. As scientists continue to unravel these complex interactions, new avenues for liver disease treatment are being explored, offering hope for innovative therapeutic strategies against liver cancer.
The condition known as bile acid dysregulation has garnered attention for its connection to the onset of liver malignancies, particularly hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). This phenomenon pertains to the abnormal processing and accumulation of bile acids within the liver, which can lead to significant organ dysfunction and inflammation. Investigators have recently identified the YAP pathway’s crucial role in this context, revealing that it can hinder the functioning of the FXR bile acid sensor. This disruption not only facilitates tumor growth but also highlights the importance of maintaining bile acid metabolism in preventing liver disease. Exploring these alternative terminologies sheds light on the broader implications of bile imbalances and their potential impact on liver health.
The Connection Between Bile Imbalance and Liver Cancer
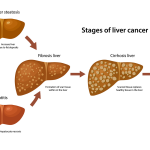
Recent research has unveiled a significant correlation between bile imbalance and the development of liver cancer, specifically hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Bile acids play a crucial role in fat digestion and metabolism, but when their production is dysregulated, it can lead to serious liver conditions. This disruption is primarily caused by the malfunctioning of the FXR (Farnesoid X receptor), which is essential for maintaining bile acid homeostasis. When bile acids accumulate in excess due to FXR’s impairment, it can provoke inflammatory responses and eventually lead to the onset of liver diseases, including HCC.
Moreover, the Hippo/YAP signaling pathway has been identified as a critical player in this imbalance. YAP, which usually promotes cell growth, acts unusually as a repressor in this context, subverting FXR’s ability to regulate bile acids effectively. This dual role of YAP complicates our understanding of liver cancer progression, as it highlights how metabolic dysregulation can serve as a precursor to cancerous changes. The implications for liver disease treatment are profound, as targeting this pathway could turn the tide against liver cancer.
Exploring Bile Acid Metabolism and Its Implications
Bile acid metabolism is a complex and vital process integral to various metabolic pathways in the liver. Disruptions in this metabolism not only contribute to liver injury but also facilitate the development of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). As the liver produces bile acid, the intricate balance maintained by receptors such as FXR becomes essential. When FXR is inhibited by factors like the YAP protein, bile acids accumulate, leading to toxic levels that can cause liver fibrosis and inflammation. Therefore, understanding bile acid metabolism offers crucial insights into liver health and disease.
Interventions that restore normal bile acid metabolism are critical in addressing liver diseases. Studies suggest that activating the FXR receptor can promote bile acid excretion and alleviate the damaging effects of bile accumulation. This not only shows promise for liver disease treatment but also opens avenues for therapeutic strategies targeting the Hippo/YAP pathway. Future pharmacological solutions that enhance FXR functionality could represent a breakthrough in managing liver cancers, highlighting the necessity of continued research in bile acid dynamics.
The Role of YAP in Tumor Formation
YAP (Yes-associated protein) has emerged as a pivotal factor in the development of liver tumors, influencing both cell growth and bile acid metabolism. Traditionally associated with promoting cell proliferation, recent findings show that YAP’s regulatory role over FXR disrupts bile acid homeostasis, leading to an environment conducive to hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) development. The intersection of YAP’s activity and bile acid regulation illustrates a significant mechanism whereby cellular signaling can directly impact cancer progression.
One of the key discoveries is how YAP’s repressive activity can cause increased bile acid production, resulting in fibrotic changes and inflammation in the liver. By identifying YAP’s unexpected role in bile acid metabolism, researchers can investigate targeted therapies that might block YAP’s repressive influence on FXR. This could provide a dual advantage: curbing tumor growth and restoring normal bile acid levels, thereby enhancing liver health and reducing the risk of cancer progression.
FXR: The Bile Acid Sensor in Liver Health
The Farnesoid X Receptor (FXR) is a crucial bile acid sensor that plays a protective role in liver health. FXR’s primary function is to regulate bile acid homeostasis, ensuring that bile acids do not reach toxic levels. When FXR is functioning correctly, it promotes the excretion of excess bile acids and suppresses their overproduction. However, dysfunctions in this receptor, often due to regulatory proteins like YAP, can lead to significant health issues, including liver cancer.
Research has indicated that activating FXR can mitigate the adverse effects of bile acid overload in the liver. Therapeutic strategies aimed at enhancing FXR activity hold great promise for improving outcomes in liver disease treatment. By stimulating this receptor, it may be possible to restore balance in bile acid metabolism, reduce liver inflammation, and ultimately impede the progression of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), showcasing the therapeutic potential of targeting bile acid signaling.
Innovative Approaches in Liver Disease Treatment
As our understanding of liver cancer and bile acid metabolism deepens, innovative treatment approaches are emerging. Research focused on the interplay between bile acids and signaling pathways such as Hippo/YAP highlights potential pharmacological solutions. Therapies that aim to enhance FXR activity or inhibit YAP’s repressive role on this critical pathway could provide new avenues for preventing the progression of liver diseases, including hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). The aim is to correct the bile imbalance that contributes to liver pathologies.
These advancements in liver disease treatment not only target the disease itself but also aim to restore overall liver function and health. With potential interventions focusing on bile acid excretion and metabolism, the future of tackling liver cancer looks promising. Continuous research and clinical trials will be essential in translating these findings into viable treatment options for patients experiencing liver complications due to bile acid dysregulation.
The Impact of Bile Acids Beyond Digestion
Bile acids are well-known for their role in fat digestion, yet their impact reaches far beyond that function. They possess hormone-like properties that influence various metabolic processes, including glucose metabolism and lipid levels. Disruptions in bile acid metabolism can lead to a cascade of health issues, particularly in relation to liver disease. By understanding these broader implications, we can appreciate the need for a holistic approach to liver health that encompasses more than just dietary adjustments.
Moreover, the emerging research suggests that maintaining normal levels of bile acids can prevent not only liver disease but also other metabolic disorders. Given that bile acids interact with numerous pathways, interventions aiming to stabilize these compounds in the liver may have widespread benefits. This highlights the necessity of continued research into bile acid dynamics and their multifaceted roles in human health, paving the way for integrative strategies to combat liver diseases.
Research Advances in Liver Cancer Understanding
Ongoing research is crucial for advancing our understanding of liver cancer and the mechanisms behind bile imbalance. Studies like those led by Yingzi Yang and her team are pivotal in elucidating the relationships between bile acid metabolism, YAP signaling pathways, and hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). By investigating these connections, researchers can identify key molecular players that contribute to liver function and disease progression, informing future therapeutic strategies.
Moreover, enhanced knowledge of the roles played by receptors like FXR in regulating bile homeostasis offers insights into potential interventions. As research uncovers the underlying mechanisms of liver cancer development, it may lead to the identification of novel biomarkers and therapeutic targets, ultimately contributing to better liver disease treatment outcomes and improved patient prognoses.
Diet and Lifestyle Factors Affecting Bile Balance
Diet and lifestyle choices significantly affect bile balance, which in turn can influence liver health. Diets high in fat and sugar can disrupt normal bile acid metabolism, leading to an imbalance that predisposes individuals to liver diseases, including hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Understanding these connections emphasizes the importance of adopting a balanced diet rich in nutrients that support liver function and bile production.
Additionally, lifestyle factors such as regular physical activity and maintaining a healthy weight play essential roles in regulating bile acid levels. Engaging in a healthy lifestyle can aid in the prevention of liver disease by ensuring optimal bile production and excretion. By promoting awareness of how personal choices impact liver health, we can foster preventive measures against liver diseases linked to bile imbalance.
Future Directions in Liver Cancer Therapies
The future of liver cancer therapies looks promising as researchers continue to explore innovative treatment options targeting bile dynamics. With the identification of key players like YAP and FXR, future therapies may focus on modulating these proteins to restore bile acid homeostasis and prevent liver damage. This could shift the paradigm from reactive treatment approaches to proactive strategies aimed at preventing liver cancer onset.
Furthermore, as we learn more about the molecular underpinnings of liver disease, personalized medicine approaches may be developed, tailoring therapies based on individual genetic and metabolic profiles. This precision in treatment could enhance effectiveness and minimize side effects, ultimately improving outcomes for patients with hepatocellular carcinoma and other liver-related conditions.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the relationship between liver cancer bile imbalance and hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC)?
Liver cancer bile imbalance plays a significant role in the development of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Disruptions in bile acid metabolism can lead to the accumulation of bile acids in the liver, causing inflammation and fibrosis, which are key factors in the progression to HCC. Understanding this relationship can help in developing targeted liver disease treatments.
How do bile acids influence liver cancer development?
Bile acids, produced by the liver, are essential for fat digestion and metabolic regulation. An imbalance, particularly in bile acid metabolism, can trigger liver inflammation and injury, contributing to the pathogenesis of liver cancers like HCC. Identifying the mechanisms behind this influence is crucial for developing liver disease treatments.
What role does the FXR bile acid sensor play in liver cancer bile imbalance?
The FXR (Farnesoid X receptor) bile acid sensor is vital for maintaining bile acid homeostasis. When liver cancer bile imbalance occurs, the activity of FXR can be inhibited, leading to excessive bile acid production and subsequent liver damage. Therapies that enhance FXR function may counteract these effects and reduce liver cancer progression.
What is the YAP tumor formation mechanism in relation to bile acid metabolism and liver cancer?
YAP (Yes-associated protein) influences tumor formation by repressing the FXR bile acid sensor, disrupting normal bile acid metabolism. In liver cancer, this repression results in elevated bile acids, promoting liver inflammation and fibrosis, which can escalate to HCC. This mechanism highlights new therapeutic targets for managing liver cancer.
Can liver disease treatment benefit from understanding bile imbalance?
Yes, understanding liver cancer bile imbalance can significantly inform liver disease treatment strategies. By targeting the molecular pathways involved in bile acid metabolism, particularly the roles of FXR and YAP, researchers are exploring new pharmacological interventions that could halt liver damage and reduce cancer risk.
What are the potential therapeutic strategies addressing liver cancer bile imbalance?
Potential therapeutic strategies to address liver cancer bile imbalance include activating the FXR bile acid sensor, inhibiting YAP’s repressive activity, and enhancing bile acid excretion. These approaches aim to restore normal bile acid metabolism, reducing inflammation and progression to hepatocellular carcinoma.
How does the study of bile acid metabolism contribute to liver cancer research?
Research on bile acid metabolism is crucial for understanding liver cancer, especially hepatocellular carcinoma. By examining key molecular switches and regulatory pathways, such as the Hippo/YAP pathway and FXR function, scientists can identify new targets for intervention, offering hope for more effective liver disease treatments.
| Key Points | Details |
|---|---|
| Bile Imbalance | Critical for digestion; an imbalance can trigger liver diseases, including HCC. |
| Study Findings | Identified a molecular switch that regulates bile acids, providing new insights for treatment. |
| Role of YAP | YAP promotes tumor formation by repressing FXR, leading to bile acid overproduction. |
| FXR Dysfunction | FXR is critical for bile acid homeostasis. Its dysfunction results in liver damage and cancer progression. |
| Potential Treatments | Strategies include enhancing FXR function and promoting bile acid excretion to combat liver cancer. |
| Research Implications | Study advances understanding of metabolic control in liver diseases, possibly informing new drug development. |
Summary
Liver cancer bile imbalance is a pressing issue in the medical community, as recent studies have uncovered the intricate relationship between bile acids and liver health. An imbalance in bile production can lead to serious liver diseases, including hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). By identifying molecular pathways like the Hippo/YAP signaling pathway, researchers hope to offer new treatment opportunities to manage this condition effectively. Understanding this dynamic not only offers hope for improved therapeutic solutions but also enhances our overall knowledge of liver physiology and disease.