Is sugar addictive? This question has sparked plenty of debate among nutritionists and researchers alike. While sugar can elicit cravings similar to those seen with addictive substances like nicotine and alcohol, its classification as an addictive substance based on clinical criteria remains contentious. Studies suggest that the human body reacts to sugar by triggering pleasure centers in the brain, leading to cravings for sugar that may feel overwhelming for some individuals. However, understanding healthy sugar consumption is crucial, as the effects of excessive sugar could lead to detrimental health issues, making it essential to recognize the importance of moderation in our diets.
The inquiry into whether sugar addiction exists is often phrased in terms of habitual behaviors and impulse control rather than traditional addiction. Cravings for sugar can manifest similarly to urges linked to drugs or alcohol, where the body reacts strongly to its presence. This phenomenon raises important questions about our food environment, especially with the prevalence of processed foods high in added sugars. As ongoing sugar cravings research reveals, the implications on health and well-being are profound, making it crucial to differentiate between healthy sugar intake and excessive consumption that may foster dependency. Engaging in this discussion allows us to consider sustainable dietary practices that can mitigate the adverse effects associated with sugar consumption.
Understanding Sugar Addiction
Sugar addiction is a term often tossed around in discussions about dietary habits. While some researchers argue that sugar may trigger cravings similar to those caused by addictive substances like alcohol and nicotine, it falls short of the clinical classification of addiction. Frank Hu, a notable nutrition expert, explains that the compulsive behavior associated with sugar intake does exist but doesn’t reach the same severity as cravings for drugs. This has led to a nuanced understanding of ‘sugar addiction’—one that acknowledges the psychological draw of sugar without labeling it as strictly addictive.
Interestingly, the prevalence of ultra-processed foods, which are laden with sugar, unhealthy fats, and sodium, contributes to this cycle of craving. The palatability and availability of these foods lead to habitual consumption, which can foster an unhealthy relationship with sugar. When individuals attempt to cut sugar from their diets suddenly, they may experience withdrawal-like symptoms, including headaches and anxiety. While sugar can induce cravings, as research suggests, the complex nature of how it affects our body is crucial to understanding its mixed role as a dietary component.
How Sugar Impacts Health
The effects of sugar on health cannot be understated, especially considering the average American consumes nearly 20 teaspoons of added sugar daily. This excessive intake not only contributes to obesity but is also linked to various health issues such as diabetes and heart disease. The American Heart Association recommends limiting sugar consumption to 9 teaspoons for men and 6 teaspoons for women, emphasizing moderation. Acknowledging these facts is vital for cultivating a healthier diet and mitigating the adverse effects of high sugar consumption.
Moreover, healthy sugar consumption involves a balance between enjoyment and mindfulness. While sugar can enhance the flavor and texture of our foods, making us feel pleasure when we eat, it’s essential to be mindful of the quantities we consume. For many, the challenge lies in avoiding added sugars present in processed snacks and beverages, which contribute to higher calorie counts without nutritional benefits. Understanding the impact of sugar on our health can empower individuals to make better dietary choices and curb those compelling cravings.
Navigating Sugar Cravings
Navigating sugar cravings can be a complex process. Many people find themselves reaching for sugary snacks or drinks in moments of stress or fatigue. This behavior could be attributed to the quick energy burst sugar provides, leading to a cycle of cravings. Research indicates that when you consume high amounts of sugar, you may find yourself craving more, making it challenging to break free from this cycle. To combat this, it’s helpful to identify triggers that lead to these cravings and develop healthier substitutes to manage them.
Additionally, gradual reduction of sugar intake can be more effective than going cold turkey, which can trigger withdrawal symptoms. Instead of eliminating sugar entirely, people might focus on decreasing added sugars and opting for more natural sources, like fruits. Incorporating mindful eating practices—such as savoring each bite and paying attention to hunger cues—can help individuals regain control over their sugar cravings. By understanding the psychology behind sugar cravings, individuals can cultivate healthier eating habits that satisfy both their dietary needs and their taste buds.
The Role of Sugar in a Balanced Diet
Sugar does play a role in a balanced diet, but understanding that role is key to nutritional health. While excessive consumption can lead to health issues, a moderate amount of sugar can enhance meals and contribute to overall enjoyment of food. Natural sugars found in fruits, whole grains, and dairy are essential for our body, providing necessary energy. They differ significantly from added sugars commonly found in processed foods, raising the question of how we can differentiate between healthy and unhealthy sugar sources.
Incorporating healthy sugar consumption into our diets involves making informed choices about the types of foods we eat. For instance, whole fruits provide fiber along with their sugars, which helps slow digestion and stabilize blood sugar levels, contrasting sharply with added sugars in candies and sodas that offer empty calories. By focusing on whole, minimally processed foods, one can maintain satisfaction without excessive sugar intake while also enjoying the sweetness that these foods provide.
Insights from Sugar Cravings Research
Recent sugar cravings research sheds light on why many struggle with sugar addiction-like behavior. Studies suggest that sugar can stimulate the brain’s reward pathways, creating a short-lived sense of euphoria similar to that caused by certain drugs. This insight helps explain why many individuals find it challenging to control their intake, often returning for more despite knowing the health risks involved. Understanding these neurological responses can help people be more compassionate towards themselves when they struggle with sugar cravings.
Moreover, this research also emphasizes the importance of addressing emotional eating, as many individuals lean on sugary snacks for comfort during stressful times. By recognizing these patterns, individuals can seek healthier coping mechanisms, such as engaging in physical activity or mindfulness practices. Thus, ongoing studies in sugar cravings not only enhance our understanding of dietary habits but also encourage strategies that promote long-term health and well-being.
The Consequences of High Sugar Intake
The consequences of high sugar intake are becoming increasingly apparent in today’s society. With average consumption soaring, the link between added sugars and chronic diseases is backed by a substantial body of research. High sugar consumption is directly associated with obesity, which is a major risk factor for a myriad of health issues, including heart disease and diabetes. The impact of sugar on metabolic health and its role in insulin resistance underscore the need for public health interventions aimed at educating individuals about the risks of excessive sugar intake.
Furthermore, beyond physical health, the implications of high sugar consumption can extend to mental health, with studies highlighting the correlation between sugar intake and mood disorders. This connection emphasizes the need for consumers to be aware of their dietary choices, particularly in how sugar-laden foods can influence their overall well-being. By understanding the full spectrum of consequences associated with high sugar intake, individuals can make informed decisions that favor both physical and mental health.
Gradual Reducing of Sugar Intake: Strategies
When it comes to reducing sugar intake, employing gradual strategies can be more effective than abrupt elimination. This approach minimizes the potential for withdrawal symptoms and psychological distress associated with cutting sugar cold turkey. One strategy involves slowly decreasing the amount of sugar added to beverages and meals over time, allowing taste buds to adjust. For instance, those who add sugar to their coffee can start by reducing the quantity a little each week until they find a level that satisfies their preferences.
Another effective method is to replace high-sugar snacks with healthier alternatives. Incorporating fresh fruits or nuts, which provide natural sugars and vital nutrients, can help quell sugar cravings without the negative health effects associated with processed snacks. Additionally, educating oneself about reading nutrition labels can empower individuals to make better choices regarding sugar consumption. By implementing these strategies, one can navigate the journey towards lower sugar consumption with greater ease and success.
Understanding the Science Behind Sugar Cravings
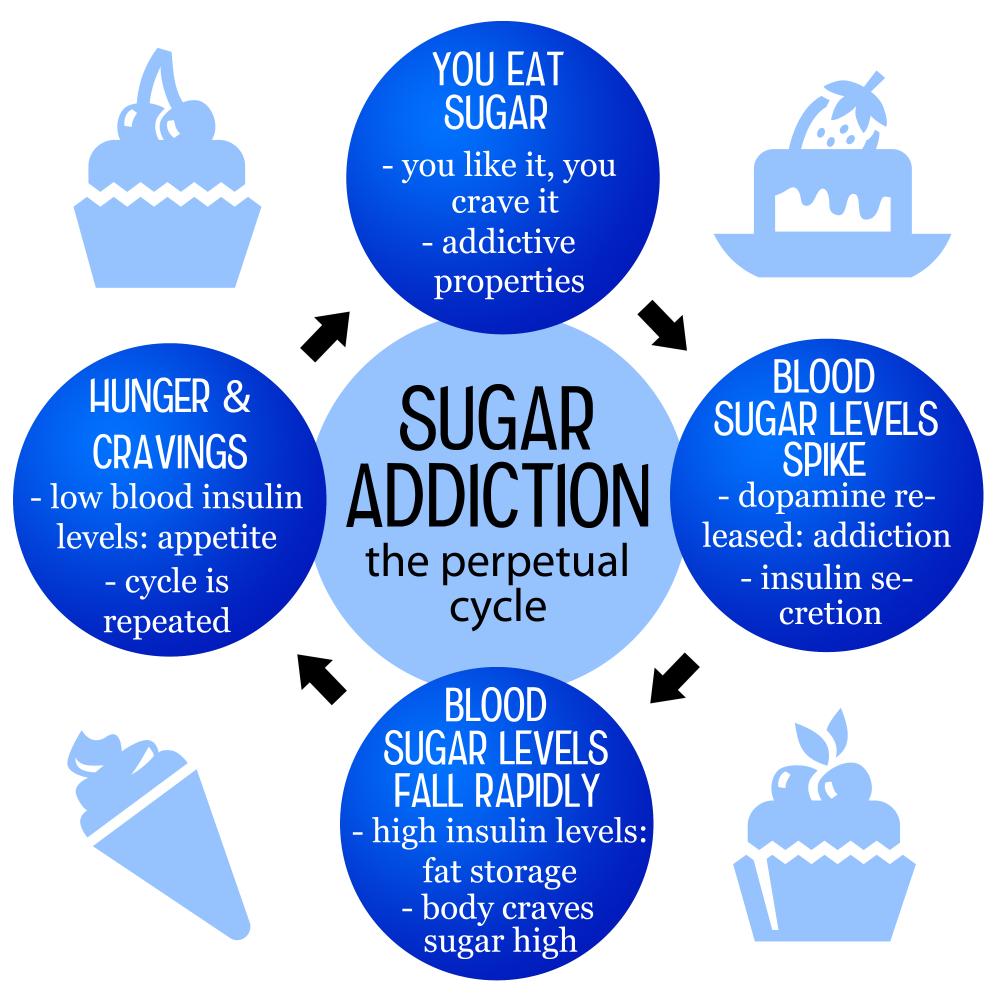
The science behind sugar cravings is a fascinating field of study that uncovers the complex biological mechanisms that drive our desire for sweet foods. Research reveals that the brain releases dopamine, a neurotransmitter associated with pleasure, in response to sugar consumption. This reaction can create an addictive cycle where individuals seek out sugar to replicate that heightened sense of happiness. Understanding this physiological response highlights the difficulty many face in regulating their sugar intake, as the brain’s reward system can overpower conscious dietary choices.
Furthermore, the metabolic effects of sugar can also play a role in cravings. Rapid increases in blood sugar levels followed by sharp declines can lead to feelings of fatigue or irritability, which often trigger a desire for more sugar. Thus, the scientific understanding of sugar cravings not only explains the pull of sweet foods but can also aid in developing strategies to break the cycle. By incorporating more stable energy sources into one’s diet, such as whole grains and proteins, individuals can experience fewer cravings and maintain balanced energy levels throughout the day.
Maintaining Moderation: Finding Balance with Sugar
Maintaining moderation in sugar consumption is essential for a healthy lifestyle. The key lies in discerning between the sources of sugar in our diets and understanding the importance of balance. It’s not about completely eliminating sugar but rather ensuring that added sugars do not dominate one’s dietary choices. By focusing on whole, natural sources of sugar, like fruits and dairy, while reducing added sugars in processed foods, individuals can enjoy sweetness without compromising their health.
Finding that balance requires thoughtful choices and mindfulness in eating. Readers are encouraged to read labels actively and be conscious of hidden forms of sugar in everyday items. Furthermore, incorporating a variety of flavors in meals can reduce the need for sugar, allowing other tastes to shine through. This holistic approach to sugar consumption fosters a healthier relationship with food, enabling individuals to savor their favorites without overindulgence.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is sugar addictive like alcohol or nicotine?
While sugar can elicit cravings similar to addictive substances, it’s not officially classified as an addictive substance like alcohol or nicotine. Sugar can increase cravings and lead to compulsive eating behaviors due to the way it’s present in many ultra-processed foods. However, the withdrawal symptoms from sugar are generally milder when compared to those of true addictive substances.
What are the effects of sugar on cravings?
Sugar has been shown to increase cravings, particularly when consumed in excess. The consumption of ultra-processed foods rich in sugar can lead to habitual eating patterns, where individuals may experience withdrawal-like symptoms if they suddenly stop consuming these foods. Therefore, it’s important to monitor your sugar intake to mitigate these cravings.
How does sugar addiction relate to healthy sugar consumption?
Understanding sugar addiction involves recognizing the balance of sugar in our diets. While some may experience strong cravings for sugar, consuming it in moderation is key to maintaining a healthy diet. The American Heart Association recommends limiting added sugar to 9 teaspoons for men and 6 for women, promoting a healthier relationship with sugar and its effects on the body.
What does sugar cravings research say about sugar addiction?
Research indicates that while sugar can trigger cravings and compulsive behaviors similar to addiction, it is not deemed an addictive substance by clinical standards. Studies on sugar cravings reveal that individuals may experience physical and psychological effects from excessive sugar intake, necessitating careful monitoring of sugar consumption.
How can I reduce cravings for sugar without feeling deprived?
To manage sugar cravings effectively, it’s recommended to gradually decrease added sugar intake rather than abruptly eliminating it. By being mindful of sugar consumption and reading food labels, individuals can strike a balance that allows for some sweetness without excessive intake, ultimately creating a healthier dietary pattern.
Are there healthy alternatives to satisfy sugar cravings?
Yes, there are several healthy alternatives to satisfy sugar cravings, such as fruit, which contains natural sugars along with fiber, vitamins, and minerals. Additionally, opting for whole grains and dairy can help fulfill cravings without reaching for added sugars in processed foods, promoting healthier sugar consumption overall.
What is the connection between sugar addiction and ultra-processed foods?
Ultra-processed foods often contain high levels of added sugar, unhealthy fats, and sodium, which can exacerbate sugar cravings and lead to habitual consumption. This relationship highlights the importance of choosing whole, minimally processed foods to help control sugar intake and reduce the risk of developing addictive-like eating behaviors.
Is it possible to completely eliminate sugar from my diet?
Completely eliminating sugar from your diet may not be practical or necessary, as sugar is present in many nutritious foods like fruits, vegetables, and dairy. Instead, focusing on reducing added sugars and practicing moderation can help maintain a healthy dietary balance without the risks associated with strict deprivation.
| Key Points | Details |
|---|---|
| Classification of Sugar | Sugar is not classified as an addictive substance according to clinical criteria. |
| Cravings and Effects | Sugar increases cravings and can trigger compulsive eating behaviors, but symptoms are less severe than for alcohol or nicotine. |
| Food System Impact | Ultra-processed foods with added sugar contribute to increased cravings and habitual consumption. |
| Psychological Effects | Withdrawal-like symptoms may occur when stopping high sugar intake, but they are less severe compared to addictive drugs. |
| Recommended Sugar Intake | AHA suggests limiting added sugar to 9 teaspoons for men, 6 teaspoons for women, and less for children. |
| Gradual Reduction | It’s recommended to reduce sugar intake gradually rather than stopping abruptly to avoid negative reactions. |
| Dietary Context | Sugar is essential in small amounts for enjoyment and should not be fully eliminated from the diet. |
Summary
Is sugar addictive? While sugar has some addictive qualities, it does not meet the strict clinical criteria for addiction like alcohol, nicotine, or drugs. Cravings for sugar are real and can lead to compulsive eating behaviors due to the prevalence of ultra-processed foods in our diet. However, the psychological and physical effects of withdrawing from sugar are less severe than those associated with classified addictive substances. Therefore, while it is crucial to be mindful of sugar consumption and recognize that moderation is key, sugar also plays a necessary role in our diets. Understanding the nuances behind sugar intake can help maintain a balanced and healthy lifestyle.